Processors
Application use a configurable and extensible pipeline of
Processors to process a request.
A processor can contribute to the response or may act as filter.
ResourceDispatch and AssetDispatch are
processor implementations to process requests for dynamic and static resources.
- Introduction
- Configuration
- ResourceDispatch
- AssetDispatch
- IpFilter
- Decompressor
- Compressor
- Writing an own processor
Introduction
The resources, controller and asset chapters showed how requests for dynamic and static resources are handled.But Civilian can't know all possible ways your application wants to process requests.
Therefore applications can customize request processing by using Processors. The application processors are arranged in a pipeline:
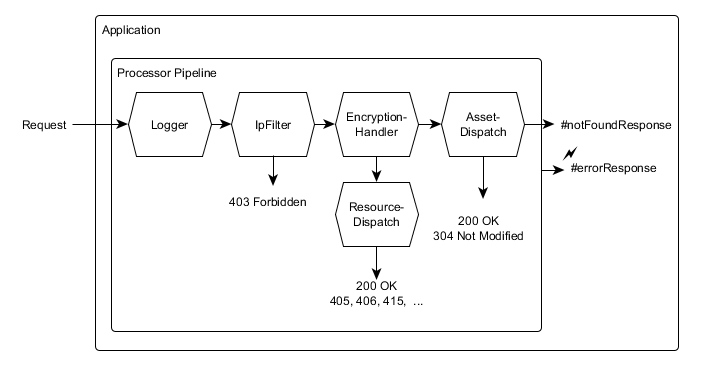
Each processor – when invoked – can decide
- whether to handle the request and contribute to the response
- to either stop further processing or invoke the next processor in the pipeline
- to do additional processing after the following processors have been invoked
- to modify request or response to implement filter functionality
Besides predefined processors you may write own implementations for special tasks. You may especially want to do this for tasks which normally would have required to implement a servlet filter.
Configuration
The processor pipeline – like all other application settings – can be configured viacivilian.ini or programmatically
during application setup: By default this pipeline is created:
- IpFilter, if the Civilian config specified a list of allowed ips
- ResourceDispatch, to dispatch requests to dynamic resources
- AssetDispatch, to serve CSS, JS files and other static resources of the application, if the application has a non empty list of asset locations
ResourceDispatch
When invoked, the ResourceDispatch processor tries to find a resource within the applications resource tree which matches the request path. As a side-effect of this matching process, path parameters are recognized and initialized in the request.If the matched resource is associated with a controller, a controller instance is created and invoked. Else the ResourceDispatch invokes the next processor in the processor pipeline.
AssetDispatch
The AssetDispatch processor uses the applications AssetService to locate an asset for the request. If it finds one, it writes the asset to the response and stops further processing. Else it just invokes the next processor in the processor pipeline.IpFilter
IpFilter is a processor implementation which blocks requests when it's remote IP is not contained in a whitelist of allowed IPs.Decompressor
Decompressor examines the request if its content is compressed: It evaluates theContent-Encoding header and recognizes these encoding schemes: gzip, x-gzip, deflate, compress, x-compress, identity.If it sees one of these schemes, it intercepts access to the request content and transparently decompresses the content.
Compressor
Compressor examines theAccept-Encoding header of the request to detect
if the response content can be be compressed.
If yes it intercepts access to the response content
in order to transparently encode the content.
Writing an own processor
To write an own processor you derive a class from Processor and add an instance to the processor pipeline during Application.initProcessors(ProcessorConfig).To implement filter functionality, you can use these techniques
- Overwrite properties of request or response.
- Intercept request or response content as demonstrated by Decompressor and Compressor
- Wrap request or response if you want to intercept access to request or response methods.
- Add a RequestStreamInterceptor to intercept reading of any request content.
- Add a RequestReaderInterceptor to intercept reading of text request content.
- Add a ResponseStreamInterceptor to intercept writing of any response content.
- Add a ResponseWriterInterceptor to intercept writing of text response content.
Additionally response interceptors can also be used to modify a response just before it is committed.